When tax filing season draws near, small business owners should know the business tax deadlines and options, such as requesting a business tax extension.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) grants extensions to file federal income business tax returns, giving businesses more time to prepare and submit their documents.
This extension applies to various types of businesses, including sole proprietors, partnerships, and corporations.
Business structures and their tax implications
When understanding small business taxes, it is essential to recognize the tax implications of different business structures.
Each business structure has its approach to handling income and earnings.
This can affect the business income tax obligations, due dates, and business tax deadlines.
Here, we focus on various business structures and how their taxes are managed.
Corporations
There are two primary types of corporations: C corporations and S corporations.
C Corporations: These corporations are taxed separately from their owners, meaning they pay corporate income tax on their profits. Additionally, corporation shareholders pay taxes on dividends, leading to double taxation.
S Corporations: In contrast, S corporations elect to have their income, deductions, and credits flow through to their shareholders, who report these items on their individual tax returns. As a result, S corporations avoid the double taxation that C corporations face. However, eligibility requirements and limitations exist to qualify as an S corporation.
Partnerships
Partnerships are businesses where two or more people share ownership, responsibilities, and profits.
In a partnership, the partners share the profits and losses of the business.
Partnerships do not pay income tax themselves; their income, deductions, and credits are divided among the partners and reported on their individual tax returns.
Limited liability companies (LLCs)
Limited Liability Companies’ business structure combines aspects of corporations and partnerships, providing limited liability protection for its owners while offering flexibility in tax treatment.
Single-Member LLC: A single-owner LLC is taxed as a sole proprietorship by default, with the owner reporting business income and expenses on their personal tax return.
Multi-Member LLC: By default, multi-member LLCs are taxed as partnerships. However, they can also choose to be taxed as either a C corporation or an S corporation.
Sole proprietorships
The sole proprietor business structure is the simplest and requires minimal legal paperwork.
The business is indistinguishable from its owner, who reports all income and expenses on their personal tax return.
The owner directly reports the income and earnings on their individual tax return using Schedule C for sole proprietorships.
Independent contractors
Independent Contractors are those self employed workers who provide services to businesses on a contractual basis.
An independent contractor reports their income and expenses on their tax returns using Schedule C, similar to sole proprietors.
Understanding the tax implications of different business structures helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions when choosing the best structure for their new venture.
The type of business entity significantly impacts how profits are taxed and distributed among the owners.
Managing estimated tax payments, deductions, and expenses for filing
Staying on top of estimated taxes, deductions, and expenses is crucial when running a business.
This ensures a smoother filing experience and can help optimize tax savings throughout the year.
Estimated tax payment
Estimated tax payments are considered quarterly taxes based on a taxpayer’s anticipated income and taxes for the year.
Businesses, the self-employed, and individuals with other sources of income need to keep up with their quarterly tax payments to avoid penalties.
Quarterly tax payment due dates
For 2024, the due dates for estimated quarterly taxes are as follows:
First quarter estimated tax payment: April 15
Second quarter estimated tax payment: June 17
Third quarter estimated tax payment: September 16
Fourth quarter estimated tax payment: January 15, 2025
The deadlines for estimated tax payments for businesses vary depending on the structure.
For example, in the case of partnerships and S corporations, the quarterly estimated tax payments are due on the 15th day of the 4th, 6th, 9th, and 12th months of the tax year.
The estimated tax payments for C corporations are due on the 15th day of the 4th, 6th, 9th, and 12th month of the tax year.
Deductions
Tax deductions can help businesses reduce their taxable income, ultimately lowering the taxes owed.
Common deductions for small businesses include home office expenses, business vehicle expenses, business insurance, and the cost of goods sold.
In 2023 and 2024, businesses can claim a tax credit of up to $7,500 when purchasing qualified electric or fuel cell electric vehicles. However, the guidelines are much stricter in 2024.
Business owners should always stay informed about changes to deductions and credits to maximize tax savings.
Turn receipts into data for tax time ✨
Try Shoeboxed’s systematic award-winning approach to receipt tracking for tax season. Try free for 30 days!
Get Started TodayExpenses
Accurately tracking business expenses is vital for deducting these costs on tax returns.
Organizing receipts, invoices, and other expense-related documentation can sometimes be overwhelming.
Thankfully, there are numerous apps and services available to simplify this process.
Shoeboxed
Shoeboxed, for example, is an expense-tracking app designed to help small businesses digitally manage their receipts for easier tax preparation.
Shoeboxed is an excellent app for keeping up with deductions for business taxes.
Companies can use such tools to ensure proper documentation of deductible expenses without the headache of manual organization.
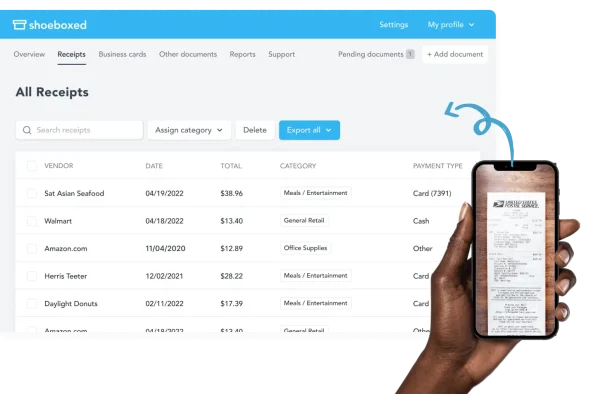
Shoeboxed’s receipt scanner app snaps pictures of receipts while on the go.
Just use their receipt tracker and receipt scanner app (iPhone, iPad, and Android) to snap pictures of receipts while on the go.
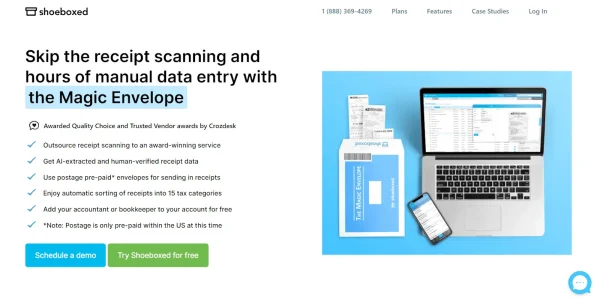
The Magic Envelope is unique to Shoeboxed.
Or, as an alternative, stuff your receipts into one of their Magic Envelopes (prepaid postage within the US), mail them, and let Shoeboxed scan the receipts and upload them into an account.
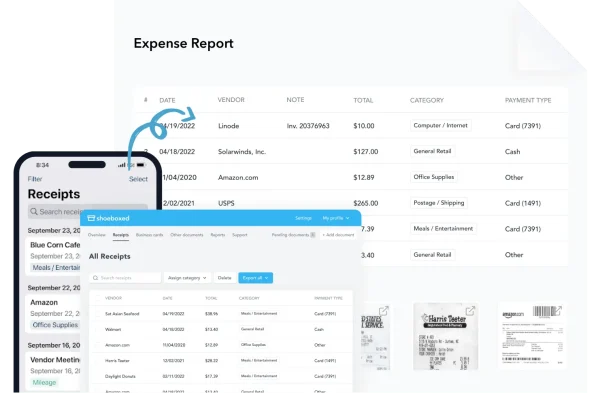
Turn data into expense reports with just a few clicks.
Receipts can be turned into data and deductibles with our expense reports, including IRS-accepted receipt images.
Shoeboxed has a built-in mileage tracker.
Shoeboxed will even keep track of business miles with its built-in mileage tracker.
By closely monitoring estimated taxes and taking advantage of deductions by diligently tracking expenses, businesses can navigate the tax landscape confidently and efficiently.
Staying informed and organized will ultimately benefit the business’s financial health in the long run.
Shoeboxed Demo by Shoeboxed YouTube
Break free from manual data entry ✨
Use Shoeboxed’s Magic Envelope to ship off your receipts and get them back as scanned data in a private, secure cloud-based account. 📁 Try free for 30 days!
Get Started TodayFiling business tax returns
It is essential to understand the various business tax forms, filing methods, and extension options available to businesses to make filing business tax forms less stressful.
Forms
Depending on their structure and tax requirements, businesses might need to file several forms by their tax filing deadline.
Common forms include the following:
Form 1040 U.S. Individual Income Tax Return with Schedule C for sole proprietors
Form 1065 U.S. Return of Partnership Income
Form 1120 U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return
Form 1120-S U.S. Income Tax Return for S Corporations
Each form serves a specific purpose in reporting the business’s income.
E-file or file electronically
E-filing is a convenient and secure method of electronically submitting tax returns, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
In fact, for the fiscal year of 2022, 11,061,140 business income tax returns were electronically filed.
Free file
The IRS offers Free File for eligible taxpayers, allowing them to prepare and e-file their federal tax returns at no cost.
Tax software programs
Additionally, various paid tax software programs can guide businesses through filing their tax forms.
Tax extensions
However, sometimes businesses might require more time to gather the necessary documents to file their income tax returns accurately.
Federal
In such situations, companies can request a tax extension by filing Form 7004 (Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns) or Form 4868 (Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return).
This extension grants an additional six months to file the federal tax return, moving the deadline to either September 16, 2024 or October 15, 2024, for the 2023 federal income tax return depending on the type of business entity.
To file an extension, multi-member LLCs, partnerships, corporations, and S corps will need to file Form 7004. Sole proprietors and single member LLCs will file Form 4868.
Here are the due dates for the extension forms:
March 15, 2024 - Form 7004 due for partnerships, S corps, LLCs taxed as a partnership or S corp.
April 15, 2024 - Form 7004 due for C corporations and LLC taxed as a C corp.
April 15, 2024 - Form 4868 due for sole proprietors and single member LLCs as well as individual tax returns.
Once the extensions are filed, the updated deadlines are as follows:
September 16, 2024: partnerships and S corporations
October 15, 2024: individual, sole proprietors, and C corps
State
In addition to federal extensions, some states also offer tax extensions.
Small businesses within these states should check with their tax agency to determine the appropriate application process and deadlines.
It is essential to remember that filing for an extension only grants additional time to file the tax return, not to pay any unpaid taxes owed.
Therefore, businesses should still pay their estimated tax liability by the original due date to avoid penalties or interest.
Special circumstances
In certain situations, taxpayers may qualify for additional time to file their small business tax returns or make payments without requesting an extension.
These exceptional circumstances often involve taxpayers affected by natural disasters, combat zones, or other emergencies.
Combat zones
Taxpayers serving in a combat zone or hospitalized due to injuries sustained while serving in a combat zone are granted an automatic extension for filing their tax returns, paying taxes, and performing other tax-related actions.
The extension period is typically 180 days after the last day of service in the combat zone or the last day of continuous hospitalization due to injuries, plus the number of days left to take action with the IRS when entering the combat zone.
Natural disasters
The IRS often provides tax relief to taxpayers affected by natural disasters, such as hurricanes, wildfires, floods, or earthquakes.
This relief may include extended deadlines for filing tax returns, making tax payments, or submitting forms and documentation.
The specific relief and deadlines will depend on the circumstances and the area impacted by the disaster.
Taxpayers should consult the IRS website or a tax professional for information on relief in their particular situation.
Disaster areas
When the President declares a region a “federal disaster area,” the IRS may grant extensions to taxpayers who reside or have a business within that area.
The extensions typically afford extra time for filing returns and making tax payments.
Sometimes, the IRS may waive penalties or interest that would otherwise apply to late filings or payments.
Special circumstances can grant taxpayers additional time to meet their tax obligations without requesting an extension.
Taxpayers in these circumstances should consult the IRS website or a tax professional for further information and guidance.
Payments and penalties
Regarding the business tax extension deadline, it’s crucial to understand the implications of not paying business taxes due on time and the potential penalties that may apply.
Tax payments must be made by the original tax deadline, even if you’ve obtained a filing extension.
Failing to make timely payments may result in penalties and interest charges.
Penalties
Business owners should pay business taxes well before the business tax deadlines to avoid penalties.
The penalty for late tax payment is typically 0.5% of the unpaid monthly taxes, with the maximum penalty reaching up to 25% of the due back tax liability.
If the tax payment is more than 60 days late, the minimum late payment penalty will be $435 or 100% of the amount due, whichever is less.
Interest
Additionally, interest charges may be levied on any unpaid tax, compounding daily from the due date until the total amount is paid.
The interest rate is determined quarterly and can vary.
Payment plans
A business that cannot pay its total tax liability in a single payment can request an installment agreement with the IRS.
Entering a payment plan can give taxpayers more time to pay the taxes in smaller portions.
However, we would like to point out that penalties and interest will continue to accrue until the total amount is paid.
Failure to make timely payments or underpaying may lead to a separate penalty for small businesses that need to make estimated income tax payments.
This penalty is calculated based on the difference between the required installment and the amount paid.
Employment taxes
Ensuring timely payment of payroll taxes is essential, as late payments or inadequate withholding could lead to additional penalties.
Employers may be held responsible for the employee and employer portions of payroll taxes if they fail to meet their obligations.
Taking the necessary steps to understand and meet tax payment deadlines is crucial for businesses to avoid unnecessary penalties and interest charges.
Adequate planning and timely action can help ensure compliance with tax regulations and minimize the financial impact of late payments.
Key tax deadlines and dates 2024
2024 brings several essential tax deadlines and due dates for businesses and individuals.
Keeping track of these important business tax deadlines throughout the fiscal year will help ensure timely and accurate filing.
Individual income tax returns deadline
April 15, 2024, marks the primary tax filing deadline, often called Tax Day.
This is the due date for most individual taxpayers to submit their 2023 tax returns or request an extension.
While an extension gives extra tax time to file, it does not provide additional time to pay any tax owed.
Estimated tax deadlines
Four quarterly estimated tax payment deadlines occur throughout 2024 for businesses following a calendar year.
These quarterly tax payment deadlines for each quarter are as follows:
First Quarter (January – March): April 15, 2024
Second Quarter (April – June): June 17, 2024
Third Quarter (July – September): September 16, 2024
Fourth Quarter (October – December): January 15, 2025
Corporations and partnerships also have specific tax deadlines to keep in mind.
Partnership and LLC
The Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) taxed as partnerships and partnership tax deadline is March 15, 2024.
A partnership will file Form 1065.
An LLC will file one of the following depending on its business structure.
Form 1040 for single-member LLCs
Form 1065 for multiple member LLCs
Form 1120S for S Corporations
Form 1120 for C Corporations
S corporation
S Corporations must submit their Form 1120S by March 15, 2024.
Deadline for Filing Taxes 2023 S Corporation by EA Tax Resolutions
C corporation
Meanwhile, C Corporations are required to file Form 1120 by April 15, 2024.
Estates and trusts
Estates and trusts filing Form 1041 must be filed by April 15, 2024.
Foreign bank accounts
Any small business or individual with foreign bank accounts must file the Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR) through FinCEN Form 114 by April 15, 2024.
Exempt organizations
Exempt organizations filing Form 990 must adhere to a May 15, 2024, deadline for submitting their forms to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Extensions
The extended tax deadline for those who file for an extension is either September 16, 2024 or October 15, 2024.
To reiterate, an extension to file is not an extension to pay taxes; any taxes owed should still be paid by the original tax deadline.
Business owners must still pay their estimated taxes by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
An extension merely postpones the filing deadline but does not extend the due date for any tax payments owed.
Frequently asked questions
What is the deadline for filing Form 7004 in 2024?
In 2024, the deadline for filing Form 7004 depends on the type of business for which you’re requesting an extension. The Form 7004 due date is March 15, 2024, for partnerships, S corporations, and LLCs taxed as partnerships or S corps. For C corps and LLCs taxed as corps, Form 7004 is due, the submission date is April 15, 2024. For sole proprietors and single member LLCs, Form 4868 is due April 15, 2024.
What is the S corp extension due date for 2024?
The S corporation extension due date for 2024 is September 16, 2024. This gives S corporations an additional six months to file taxes if they obtain an approved extension via Form 7004.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of the tax world can be daunting for businesses, but staying informed about tax deadlines, extensions, and IRS regulations is crucial for successful tax planning and compliance.
As the 2024 tax season progresses, businesses should ensure they’re well-prepared to manage their tax obligations, whether they plan to file on time or request an extension.
Caryl Ramsey has years of experience assisting in different aspects of bookkeeping, taxes, and customer service. She uses a variety of accounting software for setting up client information, reconciling accounts, coding expenses, running financial reports, and preparing tax returns. She is also experienced in setting up corporations with the State Corporation Commission and the IRS.
About Shoeboxed!
Shoeboxed is a receipt scanning service with receipt management software that supports multiple methods for receipt capture: send, scan, upload, forward, and more!
You can stuff your receipts into one of our Magic Envelopes (prepaid postage within the US). Use our receipt tracker + receipt scanner app (iPhone, iPad and Android) to snap a picture while on the go. Auto-import receipts from Gmail. Or forward a receipt to your designated Shoeboxed email address.
Turn your receipts into data and deductibles with our expense reports that include IRS-accepted receipt images.
Join over 1 million businesses scanning & organizing receipts, creating expense reports and more—with Shoeboxed.
Try Shoeboxed today!



